43++ Flow of cerebrospinal fluid through the ventricles for Desktop Background
Home » Wallpaper » 43++ Flow of cerebrospinal fluid through the ventricles for Desktop BackgroundThere Is Flow of cerebrospinal fluid through the ventricles images are ready in this website. Flow of cerebrospinal fluid through the ventricles are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the Flow of cerebrospinal fluid through the ventricles files here. Save to PDF all free photos.
If you’re looking for flow of cerebrospinal fluid through the ventricles pictures information related to the flow of cerebrospinal fluid through the ventricles topic, you have pay a visit to the ideal site. Our site always provides you with suggestions for seeing the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and locate more informative video content and graphics that match your interests.
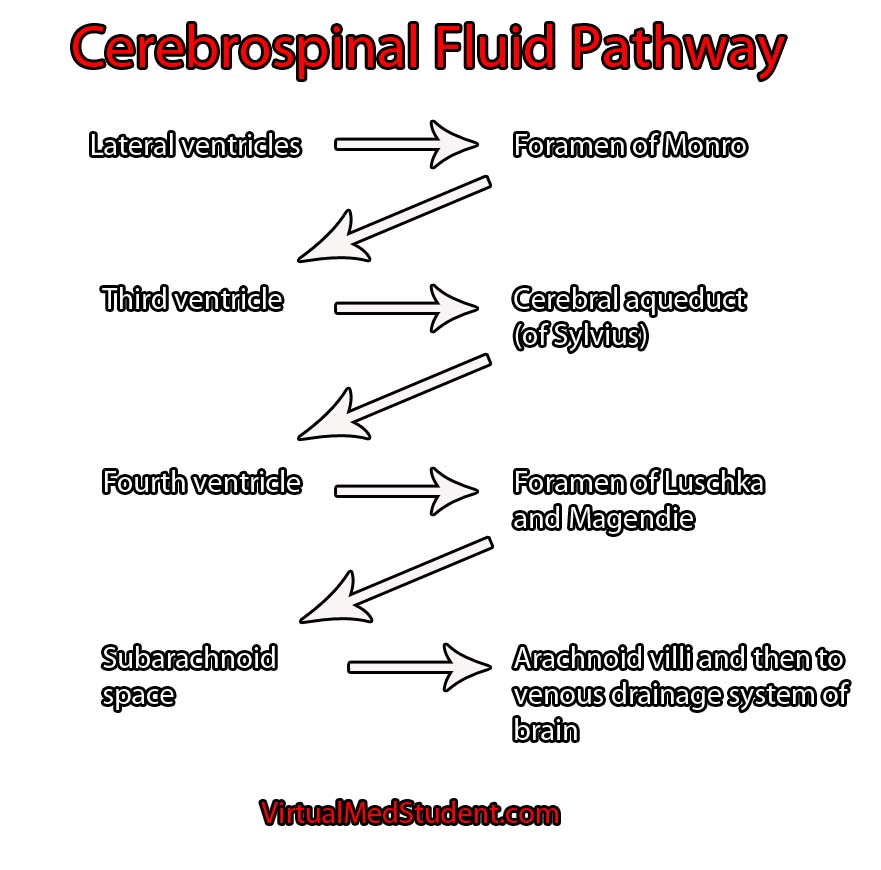
Flow Of Cerebrospinal Fluid Through The Ventricles, In this way, the exact chemical composition of the fluid can be controlled. The cerebrospinal fluid the cerebrospinal fluid (csf) fills the subarachnoid space. Csf moves from the ventricles inside the brain to the subarachnoid space outside the brain normally. The pathway of the cerebrospinal fluid is as follows:
 Click on image to zoom Cerebrospinal fluid, Tight From pinterest.com
Click on image to zoom Cerebrospinal fluid, Tight From pinterest.com
Cerebrospinal fluid is produced within the ventricles by a type of specialized membrane called a choroid plexus. The ventricles are filled with cerebrospinal fluid (csf), which provides the following functions: The csf is produced by the choroid plexus which can be found in the two lateral ventricles, and in the roof of the third and fourth ventricles. So far you know that csf flows from the lateral ventricles, into the third ventricle, passing through the cerebral aqueduct and into the fourth ventricle. Ependymal cells (one of the types of glial cells described in the introduction to the nervous system) surround blood capillaries and filter the blood to make csf.
Csf circulates through the ventricular system and subarachnoid space that surrounds both the brain and spinal cord (figure 51.21).
Csf flows internally through the ventricles, from lateral ventricles to the third ventricle to the cerebral aqueduct to the fourth ventricle. Of this volume, about 125 ml is intracranial and 25 ml of this volume lies within the ventricles. Finally it reaches the fourth ventricle through the cerebral aqueduct. Csf flows from the lateral ventricle to the third ventricle through the interventricular foramen (also called the foramen of monro). From the third ventricle, the csf flows through the cerebral aqueduct (of sylvius) to the fourth ventricle. It also extends into the ventricles of the brain, and into the central canal of the spinal cord. From there it reaches the third ventricle through the paired interventricular foramina.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Ventricles Cerebrospinal Fluid Human mechanics, Plexus Cerebrospinal fluid is produced by the choroid plexus, located in the lining of the ventricles. Ependymal cells (one of the types of glial cells described in the introduction to the nervous system) surround blood capillaries and filter the blood to make csf. It consists of capillaries and loose connective tissue, surrounded by cuboidal epithelial cells. The csf formed in each lateral ventricle flows into the third ventricle through the interventricular foramen. Csf is produced mainly by a structure called the choroid plexus in the lateral, third and fourth ventricles. Normally, csf flows out of the brain through the ventricles.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Fetal Ventriculomegaly Spinal fluid, Fetal, Spinal cord Ependymal cells (one of the types of glial cells described in the introduction to the nervous system) surround blood capillaries and filter the blood to make csf. From there it reaches the third ventricle through the paired interventricular foramina. Normally, csf flows anteriorly in the lateral ventricles through the foramen of monro and into the third ventricle. It consists of capillaries and loose connective tissue, surrounded by cuboidal epithelial cells. Cerebrospinal fluid is produced by the choroid plexus, located in the lining of the ventricles. Blockage of flow in the aqueduct can precipitate internal hydrocephalus, with swelling of the ventricles rostral to the site of blockage.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Click on image to zoom Cerebrospinal fluid, Tight This is the periaqueductal gray or central gray. Csf flows from the lateral ventricle to the third ventricle through the interventricular foramen (also called the foramen of monro). Production and reabsorption of cerebrospinal fluid. Cerebrospinal fluid is produced within the ventricles by a type of specialized membrane called a choroid plexus. Solute transport through the brain is of major importance for the clearance of toxic molecules and metabolites, and it plays key roles in the pathophysiology of the central nervous system. The route csf follows to be distributed throughout the body is known as the cerebrospinal fluid circulatory pathway.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Brain ventricle anatomy diagram Radiology Case Csf flows from the lateral ventricle to the third ventricle through the interventricular foramen (also called the foramen of monro). Cerebrospinal fluid is produced by the choroid plexus, located in the lining of the ventricles. Distributes nutritive materials to and removes wastes from nervous tissue. Csf flows from the lateral ventricle to the third ventricle through the interventricular foramen (also called the foramen of monro). Cerebrospinal fluid is produced within the ventricles by a type of specialized membrane called a choroid plexus. The csf passes through several points where blockage or obstruction could precipitate internal hydrocephalus and increased intracranial pressure.
 Source:
Source:
cerebrospinal fluid flow Neuro Pinterest It consists of capillaries and loose connective tissue, surrounded by cuboidal epithelial cells. Csf moves from the ventricles inside the brain to the subarachnoid space outside the brain normally. Csf flows internally through the ventricles, from lateral ventricles to the third ventricle to the cerebral aqueduct to the fourth ventricle. Production and reabsorption of cerebrospinal fluid. We will discuss the ventricles of the brain along with their anatomy and function, as well as the flow of cerebrospinal fluid (csf) through those structures. It flows slowly from the two lateral ventricles of the brain, where much of the fluid is formed.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Cords, Motors and Blood on Pinterest Absorbs physical shocks to the brain. The dynamics of fluid flow in normal pressure hydrocephalus (nph) are poorly understood. The ventricles are filled with cerebrospinal fluid (csf), which provides the following functions: The csf passes through several points where blockage or obstruction could precipitate internal hydrocephalus and increased intracranial pressure. What happens at stage 2? From there it reaches the third ventricle through the paired interventricular foramina.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Human brain contains four fluidfilled cavities, which are It consists of capillaries and loose connective tissue, surrounded by cuboidal epithelial cells. The single median aperture and the pair of lateral apertures connect to the subarachnoid space so that csf can flow through the ventricles and around the outside of the cns. Arachnoid vili because csf is continually being made at the rate of about 20 ml/hr, it has to exit back into the bloodstream by being reabsorbed through the _______ that protrude into the dural venous sinuses. We will discuss the ventricles of the brain along with their anatomy and function, as well as the flow of cerebrospinal fluid (csf) through those structures. It also extends into the ventricles of the brain, and into the central canal of the spinal cord. Csf continues to flow into the inner part of the spinal cord by flowing through the tiny _____ of the spinal cord, as well as around the exterior of the spinal cord in the _____ space.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Ventricular system of the brain Craniosacral therapy In this way, the exact chemical composition of the fluid can be controlled. The single median aperture and the pair of lateral apertures connect to the subarachnoid space so that csf can flow through the ventricles and around the outside of the cns. It may happen due to narrowing of the canal that connects the third and fourth brain ventricle, as a result of some hereditary diseases and congenital anatomical anomalies, as a result of newborn meningitis, bleeding in the region of the brain cells prone to prematurely born babies, after some pregnancy infections, etc. So far you know that csf flows from the lateral ventricles, into the third ventricle, passing through the cerebral aqueduct and into the fourth ventricle. Distributes nutritive materials to and removes wastes from nervous tissue. The pathway of the cerebrospinal fluid is as follows:
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Pin by Glenn Kageyama on Neuroanatomy Brain anatomy Arachnoid vili because csf is continually being made at the rate of about 20 ml/hr, it has to exit back into the bloodstream by being reabsorbed through the _______ that protrude into the dural venous sinuses. From there it reaches the third ventricle through the paired interventricular foramina. The pathway of the cerebrospinal fluid is as follows: Solute transport through the brain is of major importance for the clearance of toxic molecules and metabolites, and it plays key roles in the pathophysiology of the central nervous system. This solute transport notably depends on the cerebrospinal fluid (csf) flow, which circulates in the subarachnoid spaces, the ventricles and the perivascular spaces. Terms in this set (8) choroid plexus in the lateral ventricles produces csf.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
CSF flow and how having Chiari Malformation effects it Finally it reaches the fourth ventricle through the cerebral aqueduct. Terms in this set (8) choroid plexus in the lateral ventricles produces csf. We will discuss the ventricles of the brain along with their anatomy and function, as well as the flow of cerebrospinal fluid (csf) through those structures. Csf flows through interventricular foramina into third ventricle. This solute transport notably depends on the cerebrospinal fluid (csf) flow, which circulates in the subarachnoid spaces, the ventricles and the perivascular spaces. The route csf follows to be distributed throughout the body is known as the cerebrospinal fluid circulatory pathway.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Neurology/ neuroanatomy Circulation of Cerebrospinal The cerebrospinal fluid the cerebrospinal fluid (csf) fills the subarachnoid space. It is formed by the choroid plexuses of the ventricles. Normally, csf flows out of the brain through the ventricles. Of this volume, about 125 ml is intracranial and 25 ml of this volume lies within the ventricles. Cerebrospinal fluid is produced within the ventricles by a type of specialized membrane called a choroid plexus. What happens at stage 2?
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Image result for choroidal epithelial cells Plexus What happens at stage 1? Csf flows internally through the ventricles, from lateral ventricles to the third ventricle to the cerebral aqueduct to the fourth ventricle. We will discuss the ventricles of the brain along with their anatomy and function, as well as the flow of cerebrospinal fluid (csf) through those structures. This solute transport notably depends on the cerebrospinal fluid (csf) flow, which circulates in the subarachnoid spaces, the ventricles and the perivascular spaces. This is the periaqueductal gray or central gray. Blockage of flow in the aqueduct can precipitate internal hydrocephalus, with swelling of the ventricles rostral to the site of blockage.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Kapitola1212ENG01.jpg 2,373×1,757 píxeles Neurociencia It flows slowly from the two lateral ventricles of the brain, where much of the fluid is formed. By definition, the ventricles are cavities located within the brain that contain cerebrospinal fluid. Cerebrospinal fluid is produced within the ventricles by a type of specialized membrane called a choroid plexus. This is the periaqueductal gray or central gray. Solute transport through the brain is of major importance for the clearance of toxic molecules and metabolites, and it plays key roles in the pathophysiology of the central nervous system. It is formed by the choroid plexuses of the ventricles.
 Source: ar.pinterest.com
Source: ar.pinterest.com
Circulation of CSF Circulation of CSF Circulation of CSF This is the periaqueductal gray or central gray. The csf is produced by the choroid plexus which can be found in the two lateral ventricles, and in the roof of the third and fourth ventricles. Blockage of flow in the aqueduct can precipitate internal hydrocephalus, with swelling of the ventricles rostral to the site of blockage. Ependymal cells (one of the types of glial cells described. The csf formed in each lateral ventricle flows into the third ventricle through the interventricular foramen. Finally it reaches the fourth ventricle through the cerebral aqueduct.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The location and connections between the ventricles of the Arachnoid vili because csf is continually being made at the rate of about 20 ml/hr, it has to exit back into the bloodstream by being reabsorbed through the _______ that protrude into the dural venous sinuses. Csf circulates through the ventricular system and subarachnoid space that surrounds both the brain and spinal cord (figure 51.21). The result is a blockage of csf flow and enlargement of the third and lateral ventricles at the expense of the surrounding brain tissue. The single median aperture and the pair of lateral apertures connect to the subarachnoid space so that csf can flow through the ventricles and around the outside of the cns. Csf flows internally through the ventricles, from lateral ventricles to the third ventricle to the cerebral aqueduct to the fourth ventricle. Cerebrospinal fluid is produced within the ventricles by a type of specialized membrane called a choroid plexus.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Cerebrospinal fluid anatomical vector illustration diagram Finally it reaches the fourth ventricle through the cerebral aqueduct. However, ventricular enlargement during nph may be caused by csf backflow into the brain through the ventricles. From the third ventricle, the csf flows through the cerebral aqueduct (of sylvius) to the fourth ventricle. Finally it reaches the fourth ventricle through the cerebral aqueduct. Normally, csf flows anteriorly in the lateral ventricles through the foramen of monro and into the third ventricle. It also extends into the ventricles of the brain, and into the central canal of the spinal cord.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Pin on Craniopharyngioma The csf contains almost no blood cells, little protein, and differs from plasma with respect to the concentration. This is the periaqueductal gray or central gray. By definition, the ventricles are cavities located within the brain that contain cerebrospinal fluid. It may happen due to narrowing of the canal that connects the third and fourth brain ventricle, as a result of some hereditary diseases and congenital anatomical anomalies, as a result of newborn meningitis, bleeding in the region of the brain cells prone to prematurely born babies, after some pregnancy infections, etc. From there it reaches the third ventricle through the paired interventricular foramina. Arachnoid vili because csf is continually being made at the rate of about 20 ml/hr, it has to exit back into the bloodstream by being reabsorbed through the _______ that protrude into the dural venous sinuses.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
flow of CSF Cerebrospinal Fluid Flow Cerebrospinal The pathway of the cerebrospinal fluid is as follows: This is the periaqueductal gray or central gray. However, ventricular enlargement during nph may be caused by csf backflow into the brain through the ventricles. By definition, the ventricles are cavities located within the brain that contain cerebrospinal fluid. It flows slowly from the two lateral ventricles of the brain, where much of the fluid is formed. From the third ventricle, the csf flows through the cerebral aqueduct (of sylvius) to the fourth ventricle.
If you find this site helpful, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title flow of cerebrospinal fluid through the ventricles by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
Category
Related By Category
- 26+ Blue hibiscus flower tattoo meaning for Desktop Background
- 24++ Flower hair band images for Homescreen
- 37+ Data flow diagram examples in software engineering for Desktop Background
- 17++ Furnace air flow switch for Desktop Background
- 45++ Flow past tense meaning for Windows Mobile
- 44+ Anemone flower meaning betrayal for Android Phone
- 25+ Flower mandala coloring pages for adults for Homescreen
- 17++ Artificial flower pot price for Homescreen
- 22+ Black rose flower price for Desktop Background
- 33+ Cute flower canvas paintings for Desktop Background
